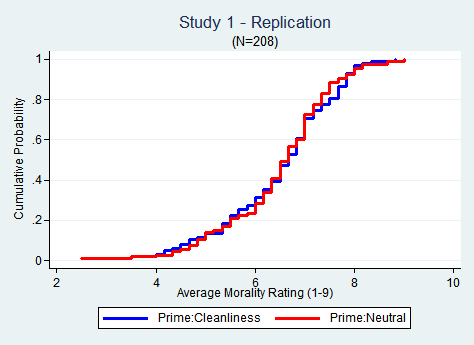
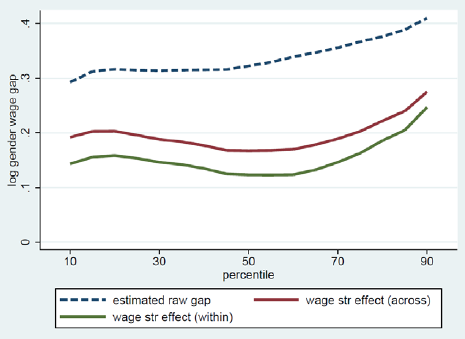
Limited variability in the data gathered on one variable may reduce the power of statistics on correlations between that variable and another variable.
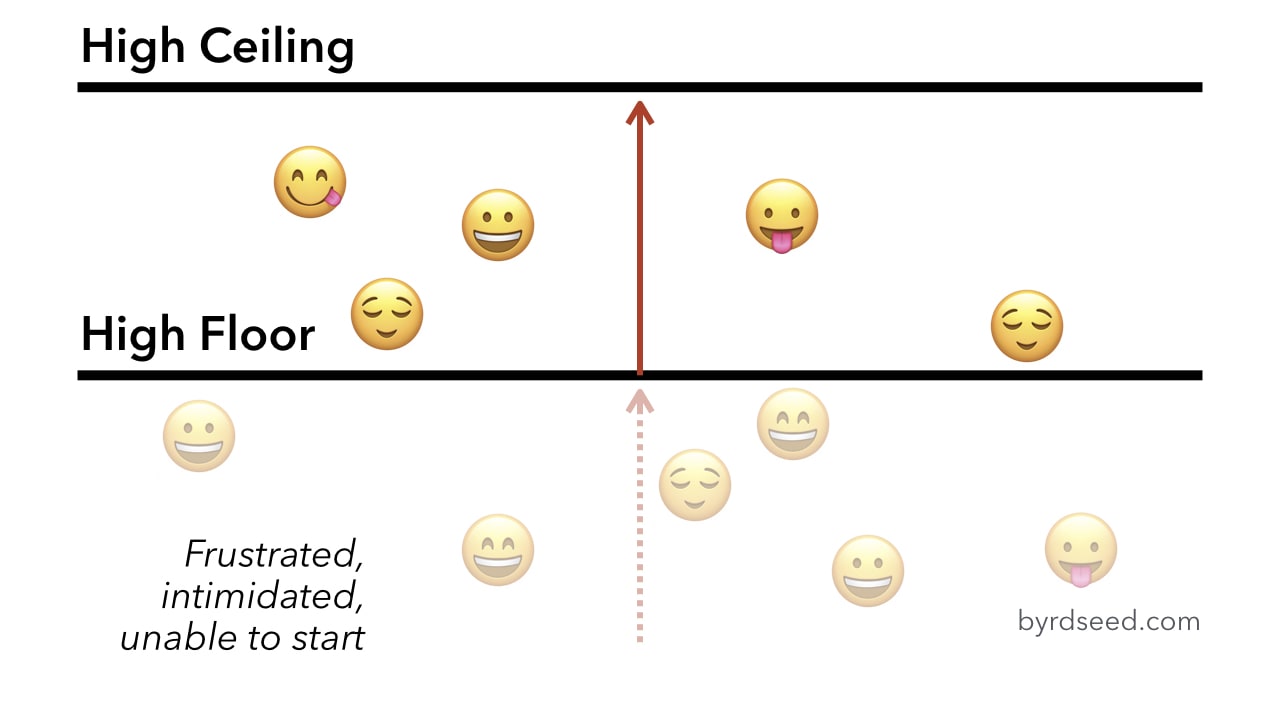
Floor and ceiling effects in research.
In layperson terms your questions are too hard for the group you are testing.
There is very little variance because the floor of your test is too high.
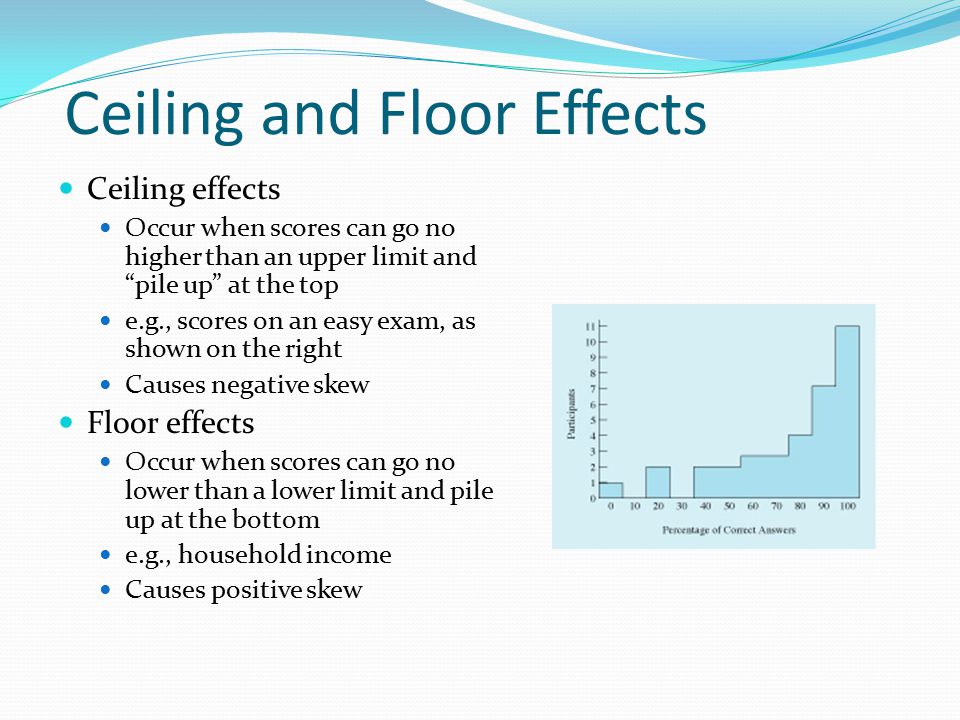
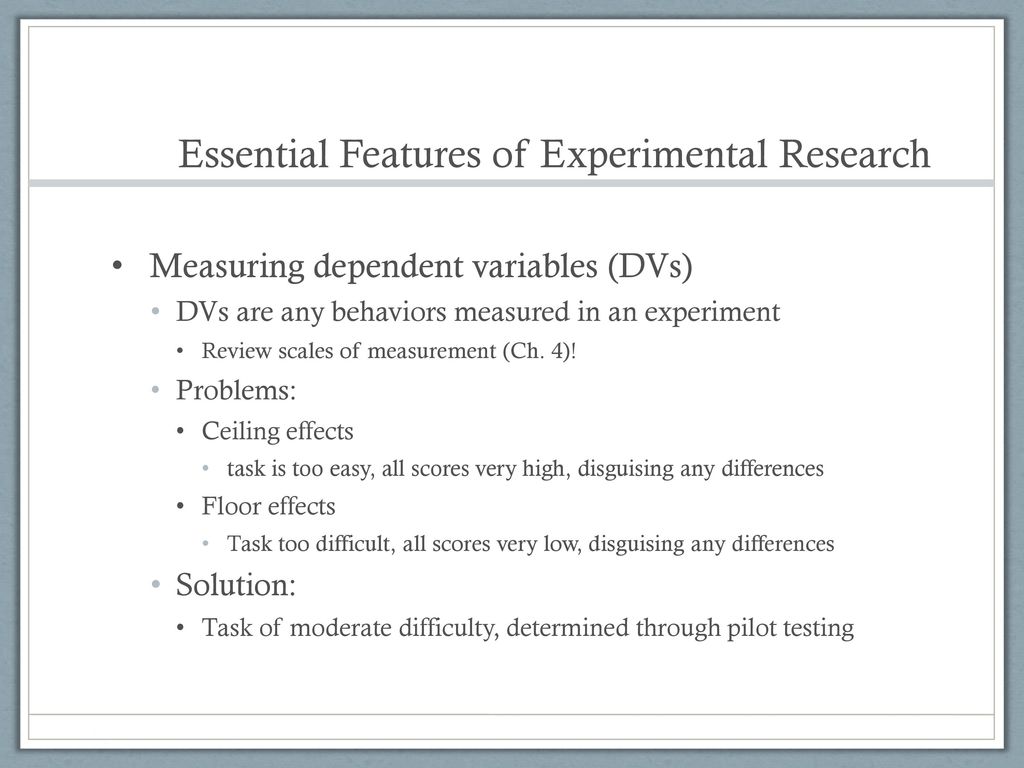
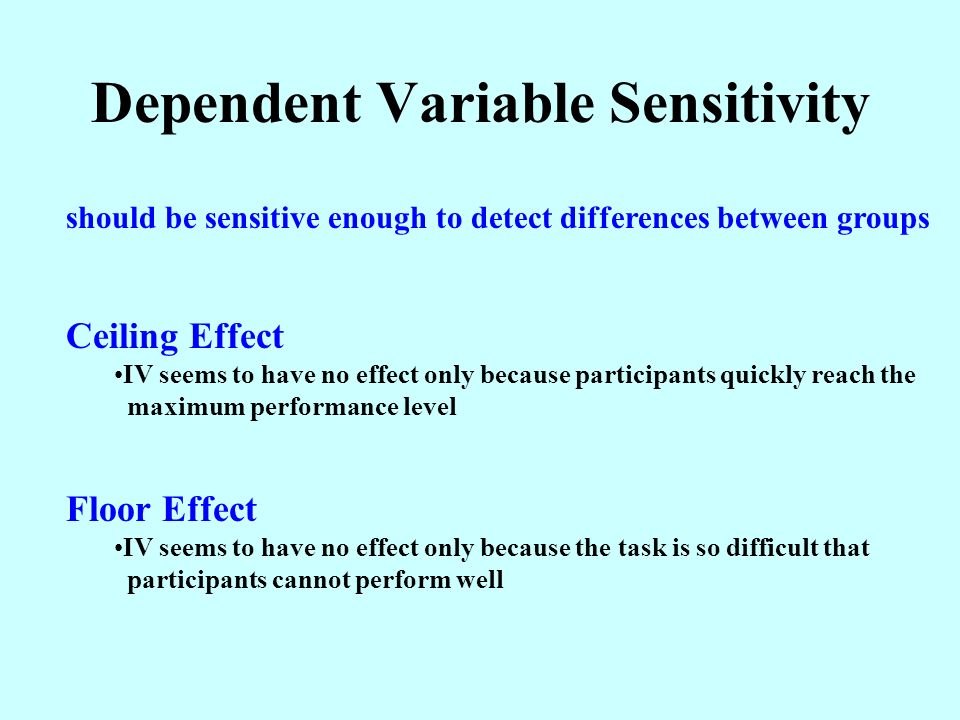
The other scale attenuation effect is the ceiling effect floor effects are occasionally encountered in psychological testing.
This research is a conceptual.
Let s talk about floor and ceiling effects for a minute.
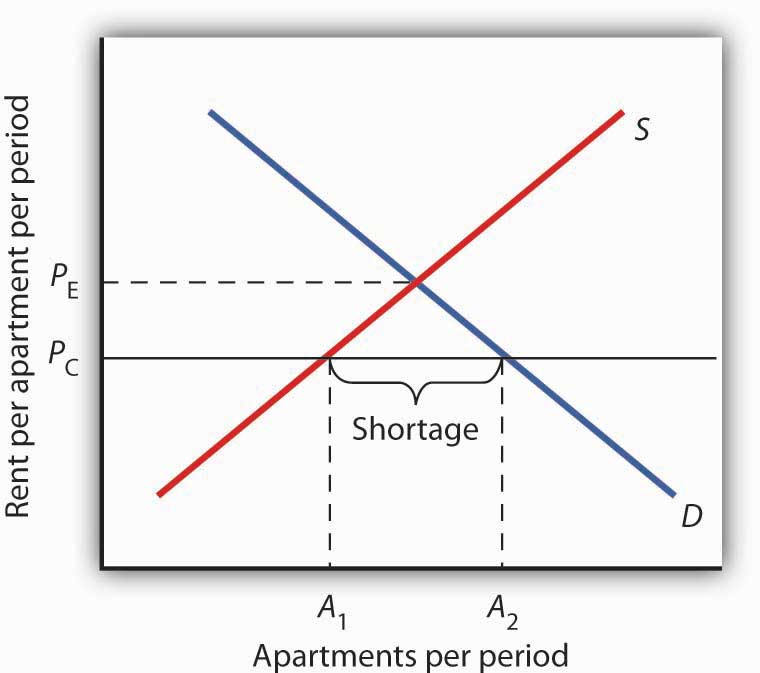
In statistics a floor effect also known as a basement effect arises when a data gathering instrument has a lower limit to the data values it can reliably specify.
Ceiling effects and floor effects both limit the range of data reported by the instrument reducing variability in the gathered data.
The term ceiling effect is a measurement limitation that occurs when the highest possible score or close to the highest score on a test or measurement instrument is reached thereby decreasing the likelihood that the testing instrument has accurately measured the intended domain.
Floor and ceiling effects were considered present if 15 of patients achieved the worst score floor effect 0 48 or best ceiling effect 48 48 score.
The inability of a test to measure or discriminate below a certain point usually because its items are too difficult.
A floor effect is when most of your subjects score near the bottom.